 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Aletris farinosa
Colic-root
State Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1
Did You Know?
One of its valuable properties is its tonic influence on the female generative organs, proving of great use in cases of habitual miscarriage.
Description
Colic-root (Aletris farinosa) is a perennial herb that grows from .5-1m in height. The leaves are narrow, lance-shaped, 5-18cm long, parallel veined, and mostly clustered at the base of the plant. The flowers, appearing from May to July, are relatively and numerous on the middle and upper part of the stem. The individual flowers are whitish, 6-10mm long, with six petal-like lobes that have a rough texture, and which persist after blooming time and enclose the capsular fruit.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey (PABS) considers colic-root to be a species of special concern, based on the very few occurrences that have been recently confirmed and its apparent decline in numbers from historical levels. It has a PA legal rarity status of Undetermined, but has been assigned a suggested rarity status of Endangered by PABS. Fewer than ten populations, mostly with few individuals, are currently known from the state.
Habitat
The species grows in a variety of habitats, including clearings and openings, thickets, open woods, serpentine barrens, and wetlands, especially on sandy or peaty substrates.
Survey Dates
Flowers May - July; distinctive flower structures July - May
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, it occurs primarily in the southeastern counties.
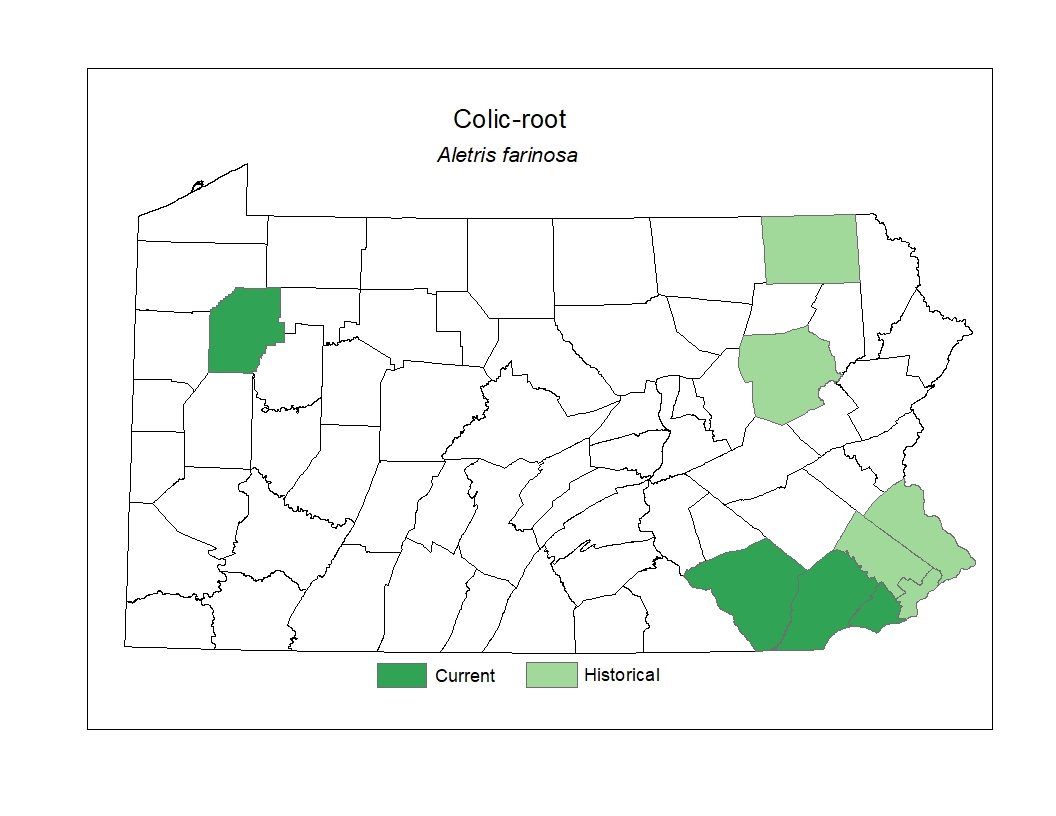
Threats
The remaining populations of colic-root in the state are threatened by human-related habitat loss, natural succession, invasive species, and collection by gardeners and herbal medicine enthusiasts.
Management
Given the preference of the species for open habitats, active management - such as fire, mowing, or invasive species removal - is often required to maintain the proper successional stage at sites where it grows.
Conservation Status Map
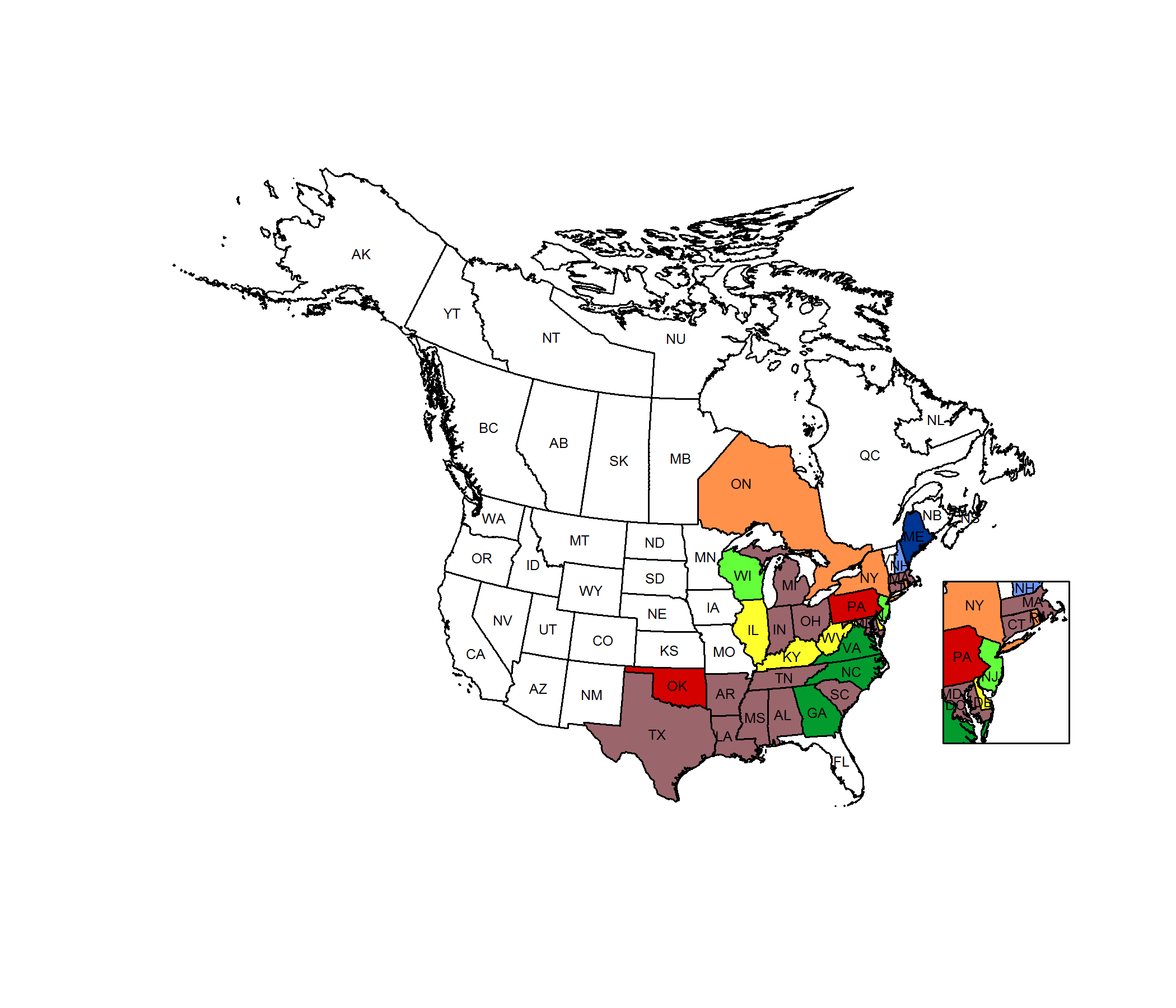
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://www.botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/u/unitru02.html
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







