 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Juncus militaris
Bayonet Rush
State Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G4
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1
Description
Bayonet Rush is a perennial grass-like herb with a rounded aerial stem that may reach 0.6 m in height, and also produces horizontal underground stems, or rhizomes. This species may grow submersed in shallow water, and the rhizome often produces an abundance of slender hairlike leaves that remain under water. The leaves of the aerial stem are much wider and thicker than the submersed leaves, having a sheathing basal portion and an elongate and linear blade that is rounded in cross-section and has a series of horizontal thickenings found at regular intervals along its length. The aerial stem tends to have just a single leaf with a well-developed blade, which often extends beyond the tip of the entire aerial stem. The minute flowers, appearing in summer, are grouped in dense clusters on the branches of the upper part of the aerial stem. Each individual flower has 6 parts that are analogous to the green sepals and colored petals found on many kinds of flowers, but in this species the parts are only 2-4 mm in length, more-or-less similar in shape to each other, vary from green to light brown to reddish, and surround the 6 stamens, or pollen producing structures within the flower. The fruit consists of dry capsule that equals or slightly exceeds the flower parts, and when mature splits open to release the microscopic 0.4-0.5 mm brownish seeds.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
Habitat
It grows on shorelines of ponds, lakes and streams, and in bogs and marshes.
Survey Dates
Flowers July - August; fruits persist into late summer or fall
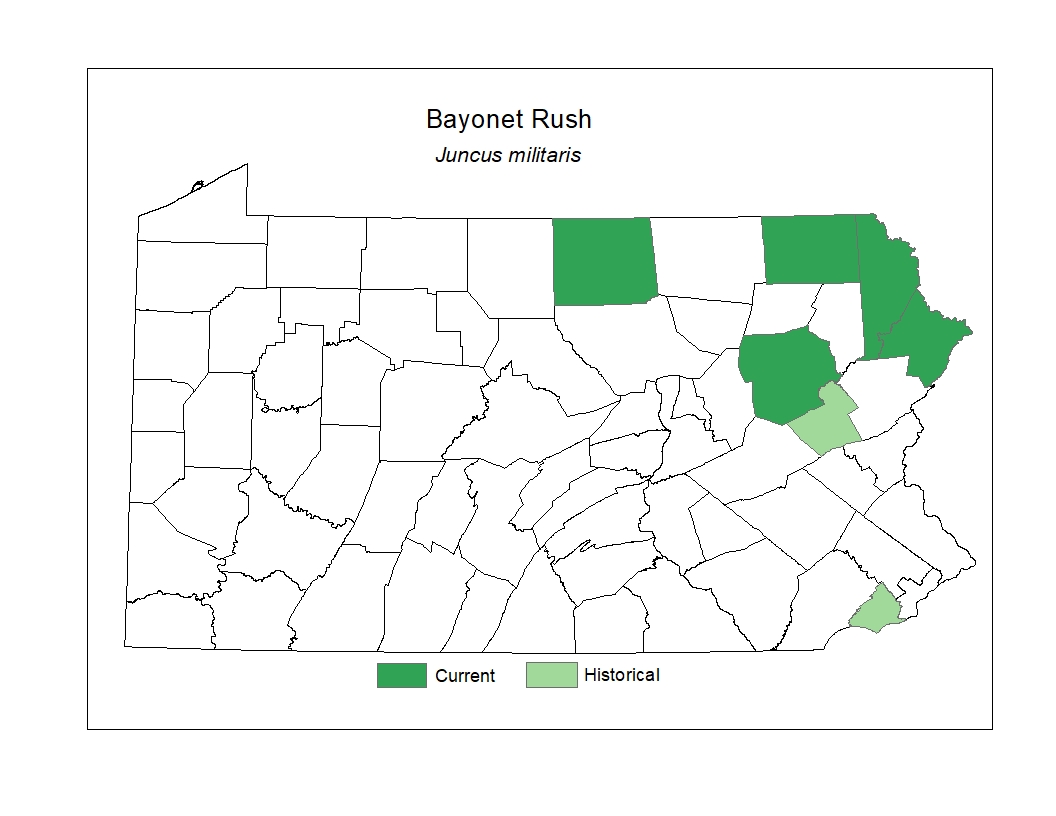
Distribution
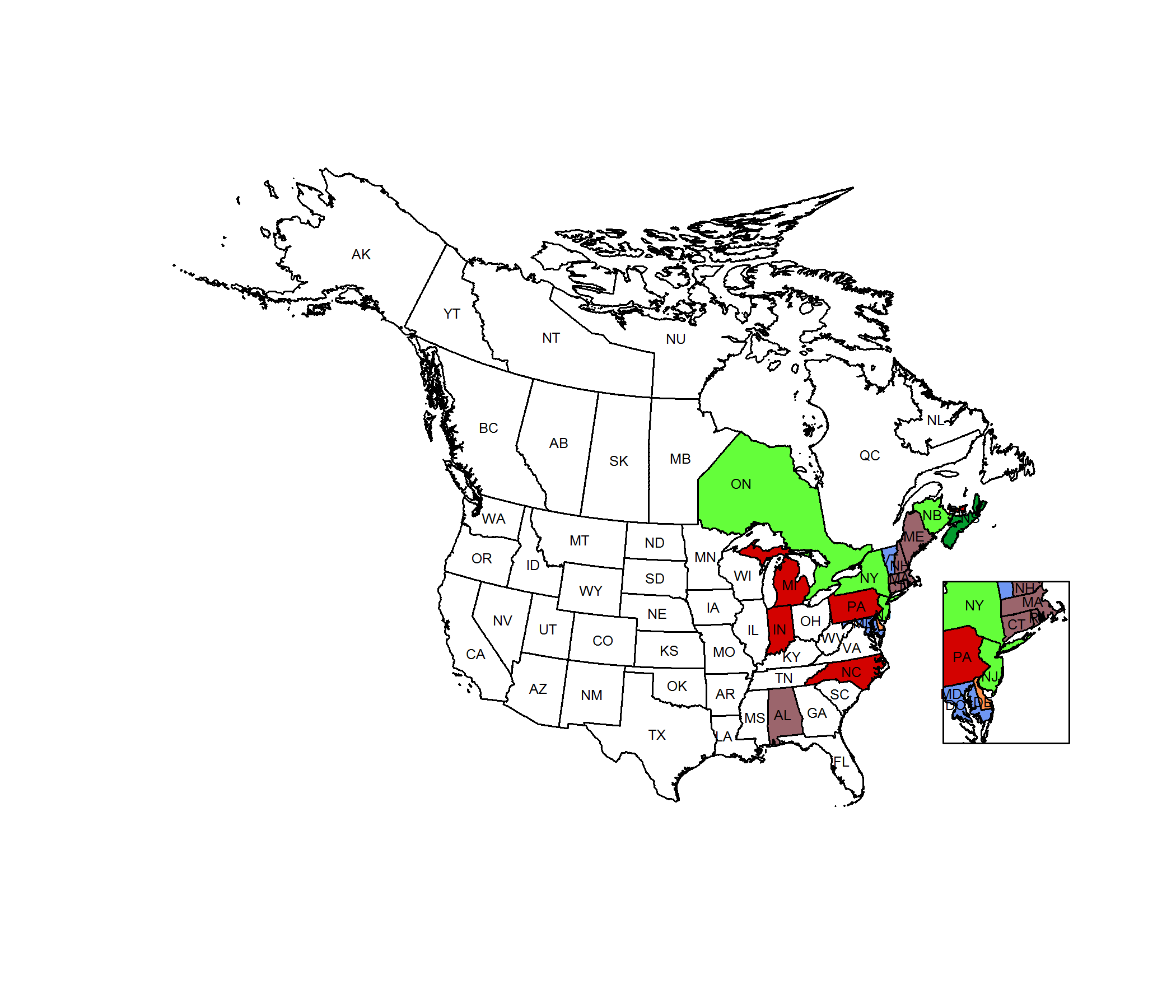
Bayonet Rush ranges from New England and Ontario south into North Carolina and Alabama. In Pennsylvania, this species has been documented historically in the northeastern counties.
Management
The viability of populations of Bayonet Rush and its habitat may be enhanced by creating buffers and protecting the natural hydrology around wetlands, controlling invasive species, and avoiding the indiscriminate use of aquatic herbicides.
Conservation Status Map
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







