 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Cyperus refractus
Reflexed Flatsedge
State Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1
Description
Reflexed flatsedge (Cyperus refractus) is a perennial herb with a triangular stem that grows from 30-80cm tall. The leaves are linear, V-shaped or flat, hairless, and up to 8mm wide. The flowers, appearing from July to August, are grouped in loose, open spikes made up of fifteen or more spikelets. Most of the spikelets extend horizontally or upward in a bottlebrush-like appearance, which helps to distinguish this species from similar species that have more downward-oriented spikelets. The spikelets are up to about 2.5cm long and covered by several overlapping scales, which enclosed the small (3mm) fruits.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey (PABS) considers reflexed flatsedge to be a species of special concern, based on the few occurrences that have been recently confirmed and its specialized habitat. It has a PA legal rarity status and a PABS suggested rarity status of Endangered. Fewer than five populations are currently known from the state.
Habitat
It grows on sandy shorelines and scoured river islands in the Susquehanna River, and elsewhere in dry woods.
Survey Dates
Fruits July - September
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, this species reaches a northern border of its known range and has been documented historically in a few southeastern counties.
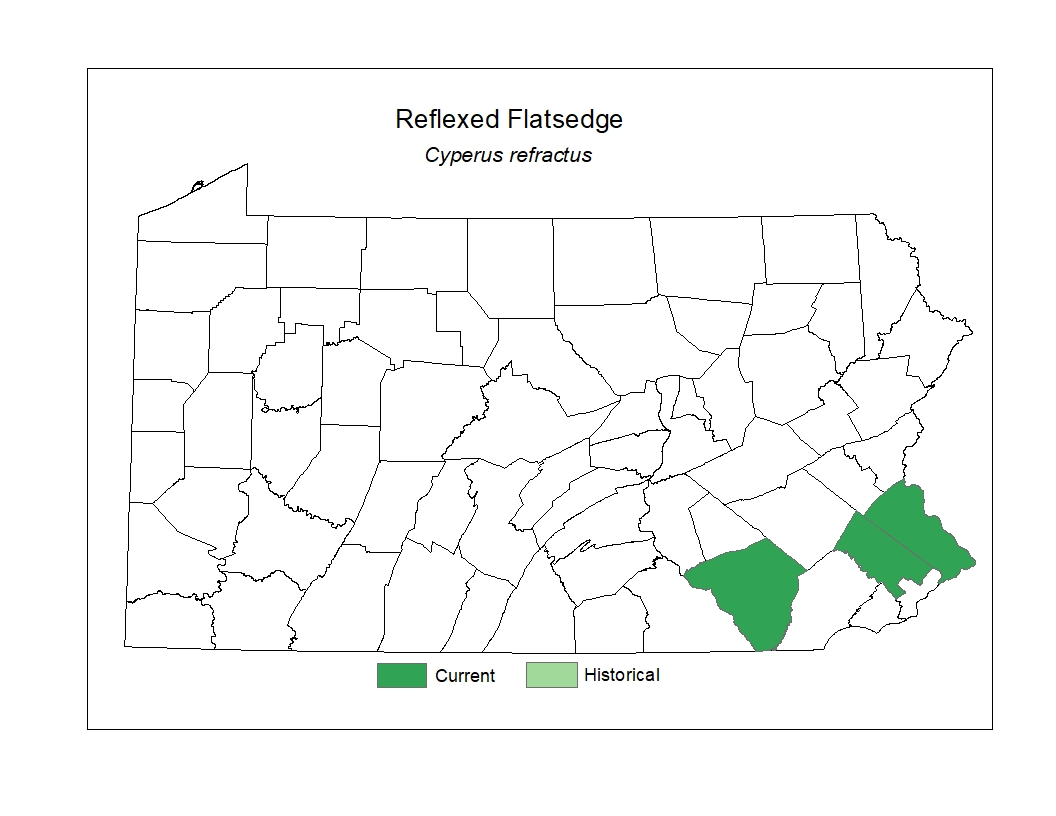
Management
The viability of the riverine populations of reflexed flatsedge and its habitat will require maintaining the natural hydrology of the Susquehanna River, with its seasonal fluctuations in water levels, as well as retaining the natural conditions of the shorelines and islands. In upland sites, given the preference of the species for relatively open habitats, active management such as fire, mowing, or invasive species removal may be required to maintain the proper successional stage.
Conservation Status Map
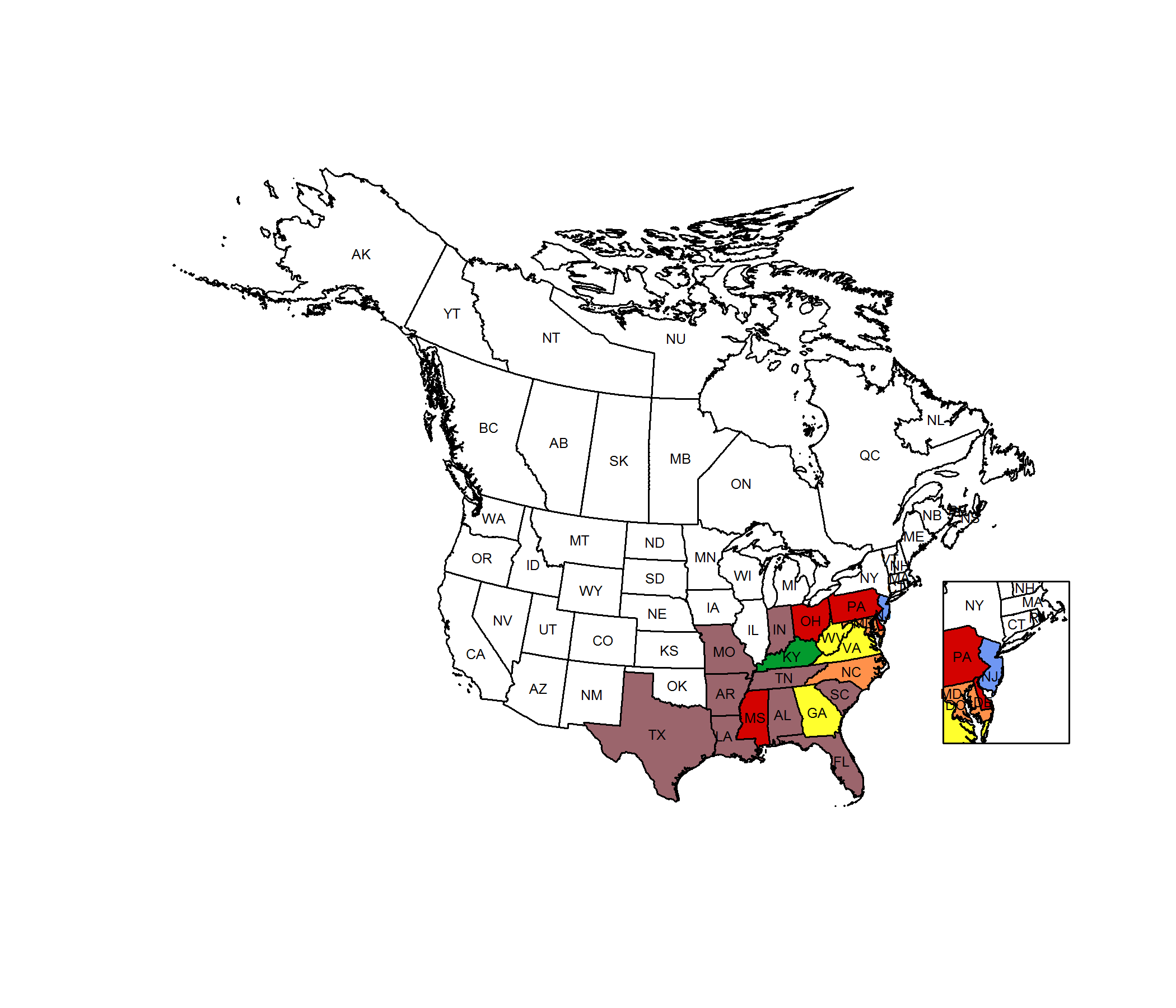
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







