 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Carex meadii
Mead's Sedge
State Status: TU
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Threatened (PT)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S2
Did You Know?
This sedge is unusual in forming loose colonies of plants from long rhizomes, rather than tight tufts of leaves from short rhizomes.
Description
Mead's sedge (Carex meadii) is a grass-like perennial herb with a three-sided stem that reaches 15-60cm in height. The leaves are linear, flat, up to 6mm wide, and arise from brownish sheaths found on the lower portions of the stem. The individual flowers are minute and unisexual, with the male flowers grouped in a club-shaped spike at the top of the stem and female flowers grouped below in one to three cylindrical spikes. The female spikes support eight to thirty sac-like structures, or perigynia, which enclose the three-sided fruit. The fruits mature in late spring and summer.
Rank Justification
Imperiled in the nation or state because of rarity due to very restricted range, very few populations (often 20 or fewer), steep declines, or other factors making it very vulnerable to extirpation from the nation or state.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey (PABS) considers Mead's sedge to be a species of special concern, based on the few occurrences that have been recently confirmed and its specialized habitat. It has a PA legal rarity status of Undetermined and has been assigned a suggested rarity status of Endangered by PABS. Fewer than fifteen populations are currently known from the state.
Habitat
It grows in damp or seasonally wet meadows, grasslands, and marshes, particularly on serpentine or diabase substrates.
Survey Dates
Fruits in June
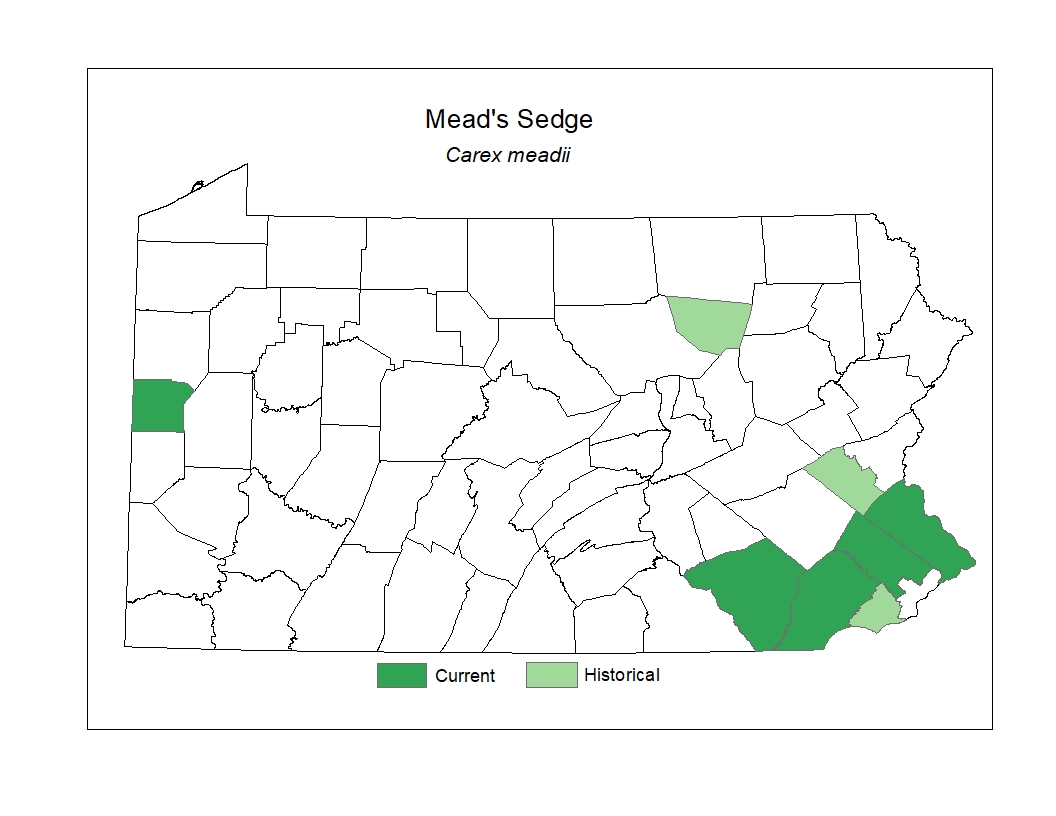
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, it has been documented historically in scattered counties.
Management
The viability of populations of this species and its habitat may be enhanced by creating buffers around wetlands, controlling invasive species, and protecting the natural hydrology around wetlands. Active management – such as fire, mowing, or invasive species removal – may be required to maintain the proper successional stage at sites where it grows.
Conservation Status Map
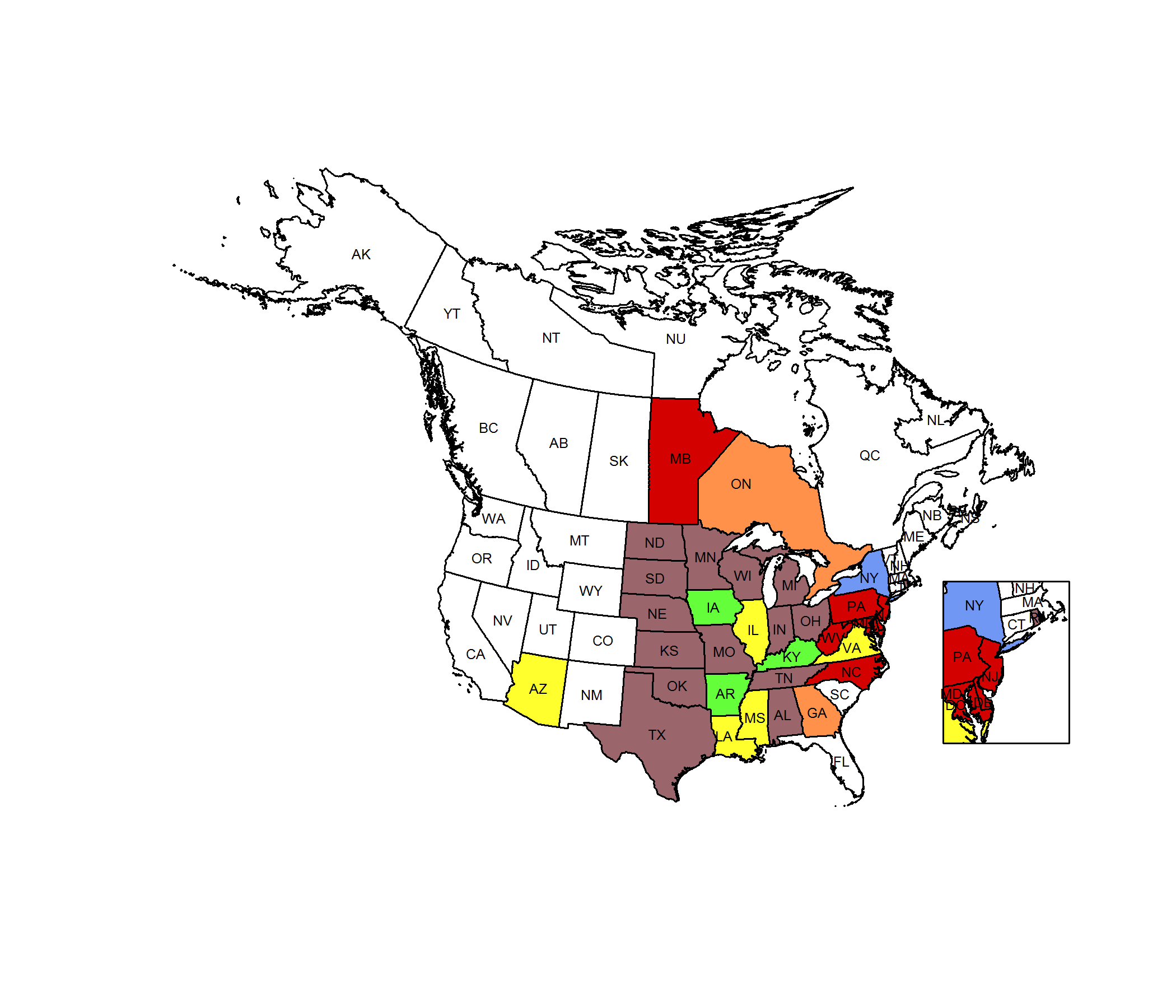
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/grasses/plants/mead_sedge.htm
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







