 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Carex limosa
Mud Sedge
State Status: TU
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Threatened (PT)
Federal Status:
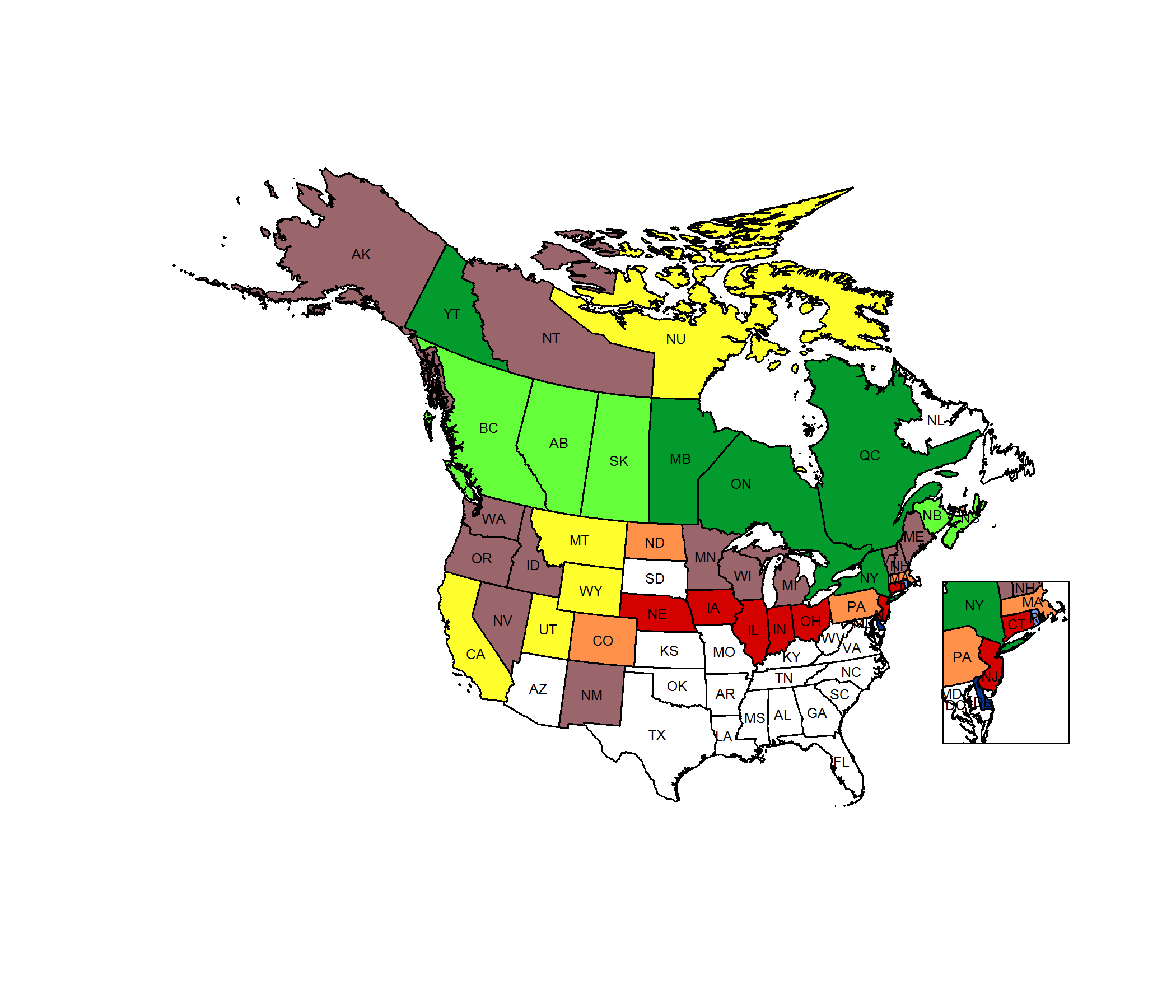
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S2
Description
Mud Sedge is a grass-like plant that forms patches in boggy places due to its wide-spreading underground stems or rhizomes. The aerial stems are triangular in cross-section and may grow to 0.6m in height but are usually much shorter, sometimes only a few inches. The leaves have linear, elongated blades that are smooth, pale green, untoothed on the margin and to about 3 mm in width. The flowers, appearing in May to July, are minute and are grouped in male or female clusters, with the usually single and stalked male cluster in an erect position at the top of the stem and the female clusters, on slender drooping stalks and numbering from 1 to 3, farther down the stem. The female cluster consists of individual inflated sac-like structures, or perigynia, which are about 3 mm in length and contain 1 flower and later 1 three-sided fruit. In this species the individual perigynia are subtended and mostly hidden by small bracts.
Rank Justification
Imperiled in the nation or state because of rarity due to very restricted range, very few populations (often 20 or fewer), steep declines, or other factors making it very vulnerable to extirpation from the nation or state.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey (PABS) considers Mud Sedge to be a species of special concern, based on the limited number of locations recently confirmed and the bog habitat. It has a PA legal rarity status of Tentatively Undetermined and a PABS suggested rarity status of Threatened.
Habitat
The species grows in bogs, especially on floating sphagnum moss mats around bog pools.
Survey Dates
Flowers, fruits June - August
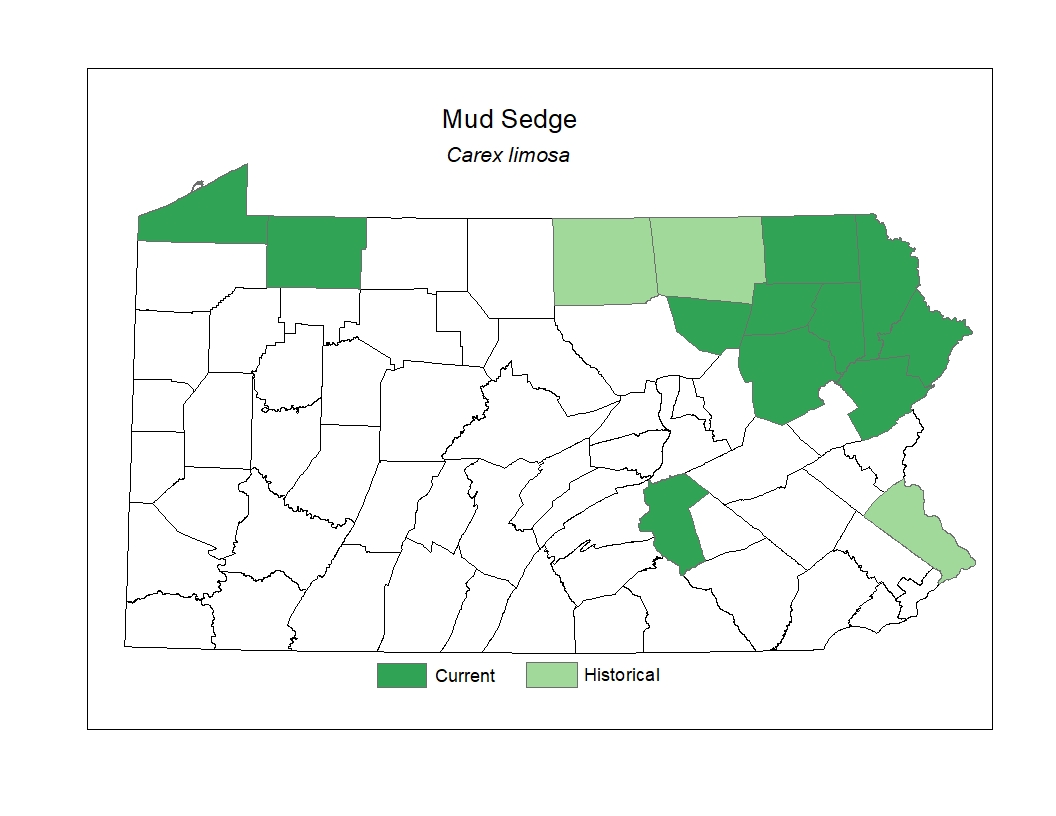
Distribution
Mud Sedge has a transcontinental range across the cooler regions of North America. In Pennsylvania, this species is considered a northerly species and has been documented historically mostly in the glaciated northeastern counties.
Management
The viability of populations of Mud Sedge and its habitat may be enhanced by creating buffers and protecting the natural hydrology around bogs. Mud Sedge is an indicator for bog habitats that feature various orchids, insectivorous plants such as sundew, bladderwort, and pitcher plant, and other interesting species.
Conservation Status Map
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







