 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Pinus echinata
Short-leaf Pine
State Status: N
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Threatened (PT)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1S2
Did You Know?
Turpentine can be obtained from the resin of all pine trees and used as an antiseptic, diuretic or rubefacient.
Description
Short-leaf pine (Pinus echinata) is an evergreen coniferous tree that may grow 25-30m tall, often with much of the trunk free of lateral dead branches. The bark is reddish-brown and forms scaly plates. The leaves are evergreen, needle-like, in bundles of two or occasionally three, from five to 12cm long, relatively slender, and tend to be straight or only slightly twisted. The cones are narrowly egg-shaped, 4-6cm long, and made up of thin scales that are spirally arranged and have a thickened tip with a short, sharp spine. The cones may persist on the tree for several years.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
Habitat
It grows mainly in well drained upland woods and slopes.
Survey Dates
Year-round (evergreen)
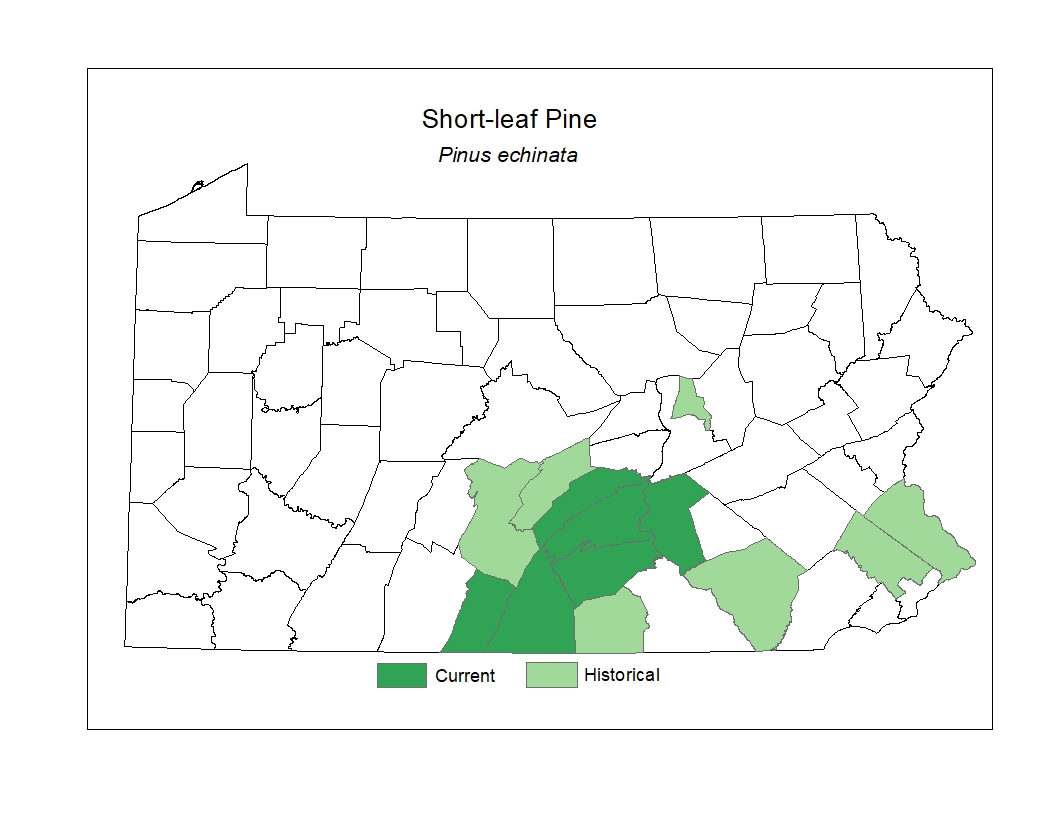
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, where it reaches a northern border
of its range, the occurrences are primarily in the southcentral counties.
Management
More field surveys are needed to determine the range, abundance, and ecological requirements of short-leaf pine. Based on current data, the long-term viability of occurrences will probably require special management, such as prescribed fire, since the species is very intolerant of shade and early successional conditions are necessary for establishment of seedlings.
Conservation Status Map
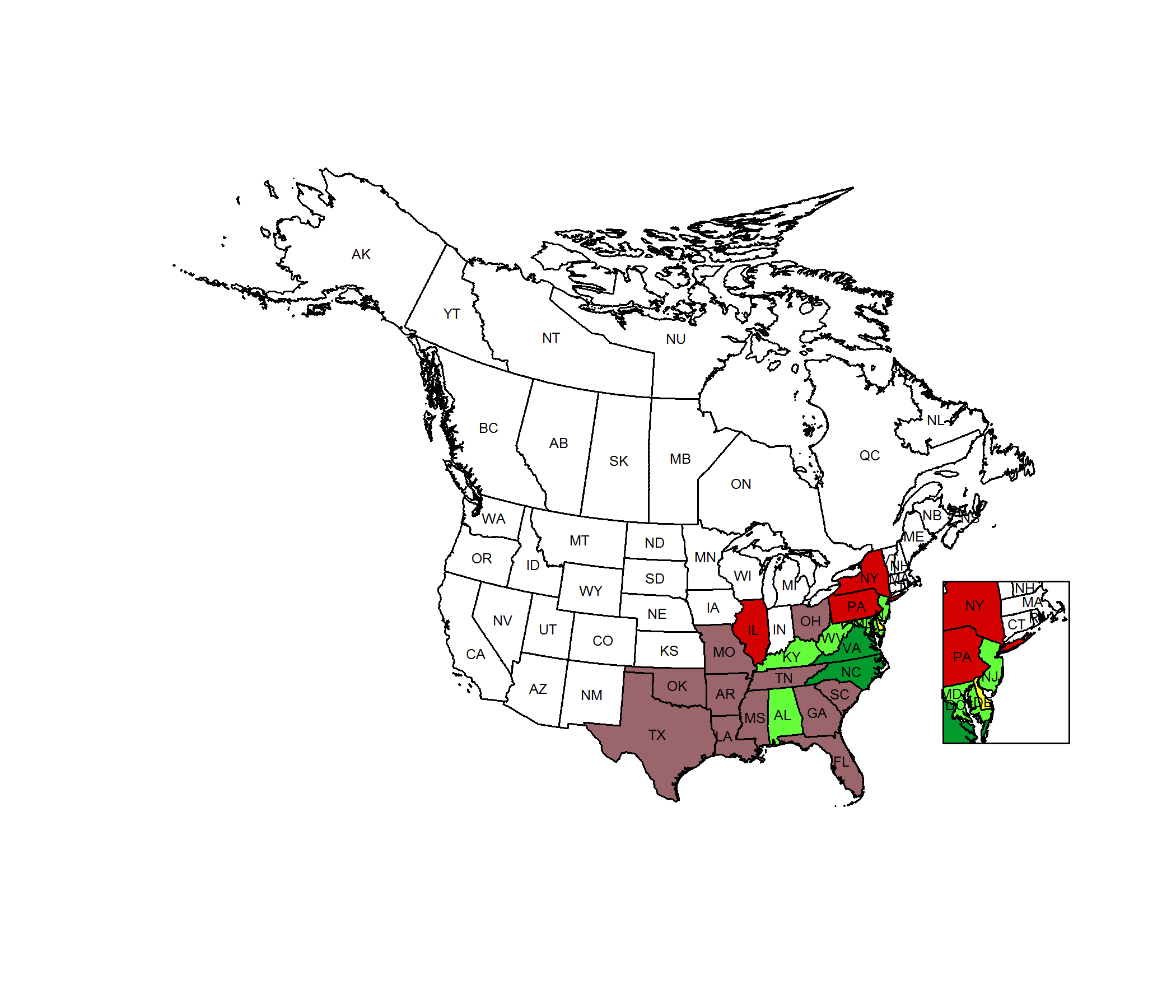
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://practicalplants.org/wiki/Pinus_echinata
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







