 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Passiflora lutea
Yellow Passionflower
State Status: Pennsylvania Threatened (PT)
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Threatened (PT)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S2
Did You Know?
This species is a major food source for many species of butterfly larvae - the pollen is the only known larval food of the passionflower bee.
Description
Yellow passionflower (Passiflora lutea) is a perennial herbaceous vine, climbing or trailing to lengths of around three meters.
Rank Justification
Imperiled in the nation or state because of rarity due to very restricted range, very few populations (often 20 or fewer), steep declines, or other factors making it very vulnerable to extirpation from the nation or state.
Habitat
Yellow passionflower grows in wet conditions; it is considered a national wetland indicator species.
Survey Dates
Flowers July - August; fruit October; distinctive leaves May - October
Distribution
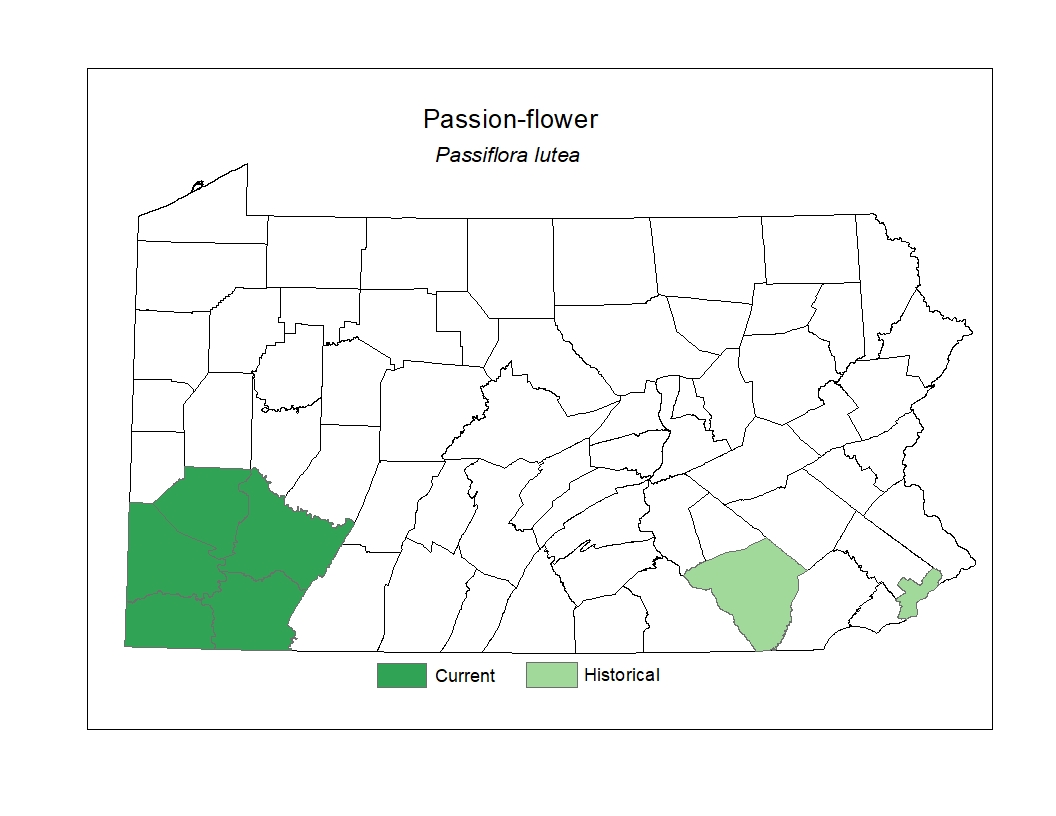
Threats
The two states in which yellow passionflower is classified as critically imperiled, Kansas and Pennsylvania, are both at the edges of its range. It is possible, then, that populations in these states are small and scattered in part because they are at the edge of the species' ecological tolerances. However, yellow passionflower's wetland habitat is frequently the target of human disturbance, including drainage and indirect modification by flood-control regimes. Probably yellow passionflower would be more abundant given more wetland habitat, even at the edges of its natural range.
Management
Yellow passionflower's status has yet to be determined through the majority of its natural range; further study of this species' abundance, especially in states at the edges of its range, would be invaluable in planning its conser-vation. Generally speaking, yellow passionflower will benefit from preservation of its wetland habitat and man-agement of invasive competitors such as Japanese honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica).
Conservation Status Map
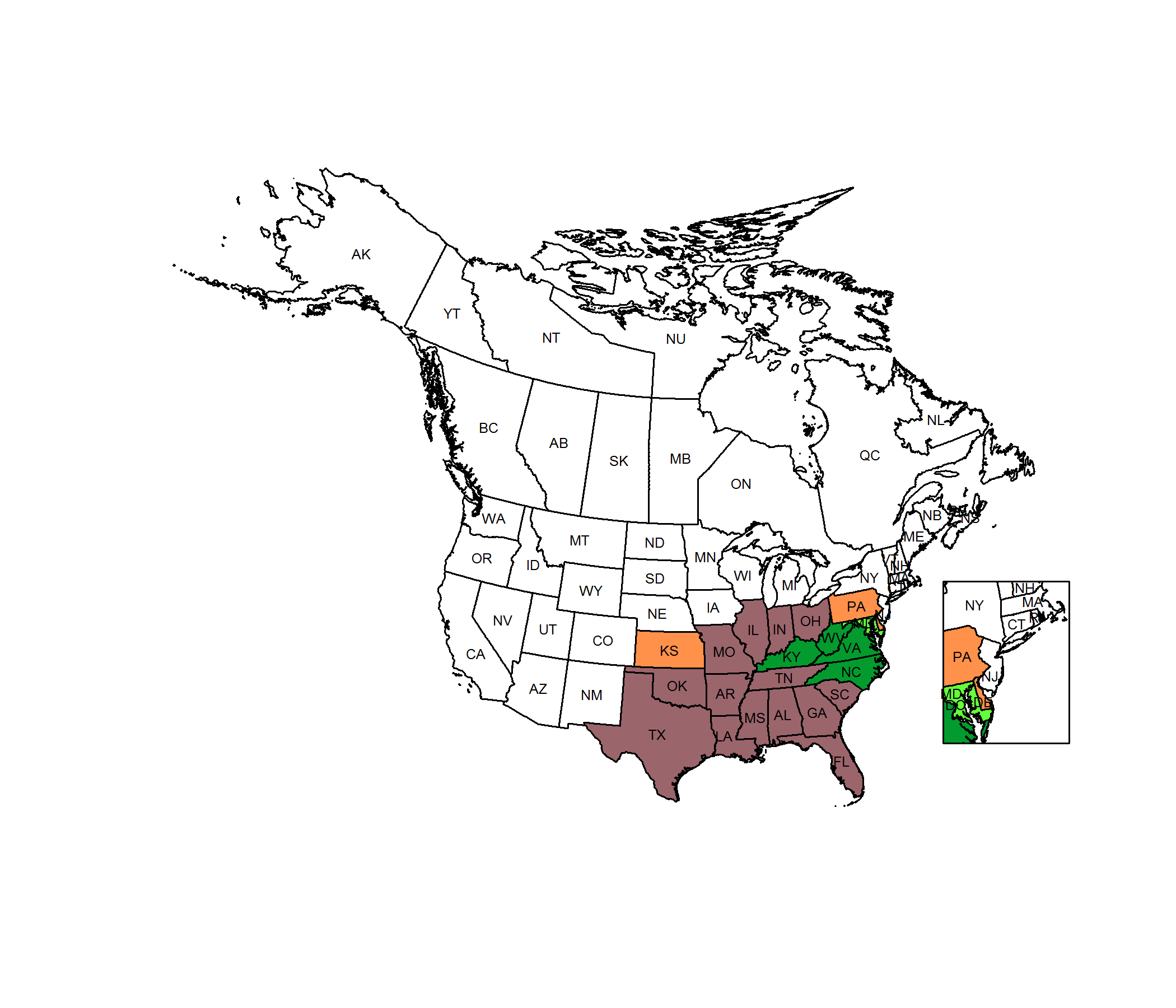
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=palu2
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







