Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Corydalis aurea
Golden Corydalis
State Status: N
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1
Did You Know?
Externally it is used as a lotion on backaches, hand sores, etc. and as a gargle for sore throats.
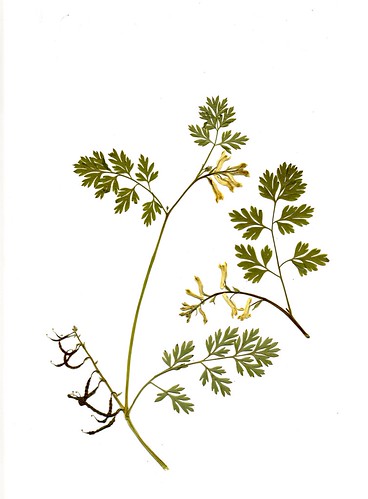
Description
Golden corydalis (Corydalis aurea) is an annual or biennial herb with upright or trailing, fleshy stems that are 15-60cm long. This spring wildflower belongs to the same family as bleeding-heart. The leaves grow both from the base of the plant and alternately along the stems. The leaves are pale green, smooth and finely divided. The flowers are yellow and 12-20mm long. They are irregular, made of four unequal petals that are partly fused near the base. The uppermost petal has a sac-like projection near the base and is not crested at the tip. Flowers are held in small clusters and bloom from May to July.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey considers golden corydalis to be a species of special concern, based on the very few occurrences that have been confirmed and the specialized and infrequent habitat. It has been assigned a rarity status of Endangered.
Habitat
It grows in rocky or sandy soil in open woods or along roadsides.
Survey Dates
Flowers May - July
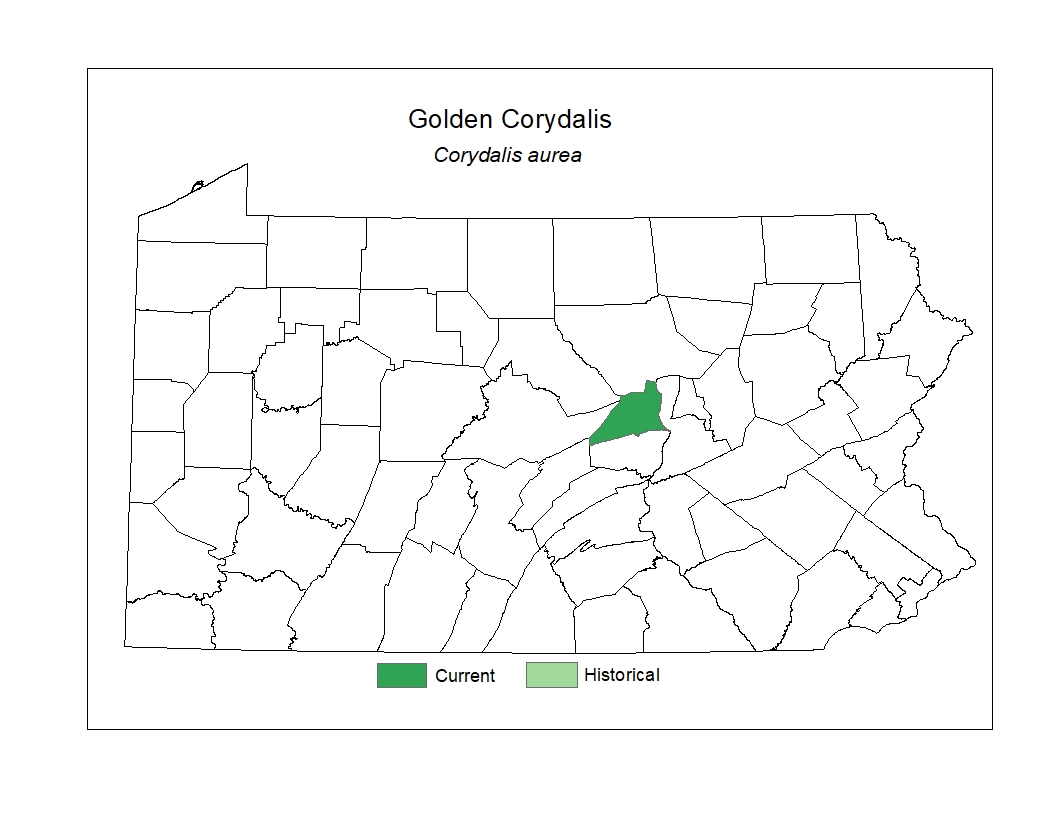
Distribution
Golden corydalis occurs throughout the western United States. In the eastern U. S. its range extends from Vermont and New Hampshire south to West Virginia.
Threats
Throughout the range of this species, habitat loss, land conversion for development, and displacement by invasive species have all played a part in its decline. In some cases, the communities where this species grows are themselves rare or have succeeded into a different community types due to the overgrowth of woody species and invasive species.
Management
Maintenance of known populations and preservation of the rare communities where golden corydalis grows will be crucial to its survival. Removal of overgrowth and invasive species will help to preserve the integrity of the sites. Management of known sites requires long term monitoring of populations. Potential sites for restoration should be evaluated.
Conservation Status Map
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://keys2liberty.wordpress.com/tag/corydalis-aurea/
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.