 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Quercus falcata
Southern Red Oak
State Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G5
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1
Did You Know?
Due to its strength this species is used for fence posts, fuel and other general construction projects.
Description
Southern red oak (Quercus falcata) is a deciduous tree that may grow to 25m in height. The bark is gray and furrowed. The leaves are alternately arranged, broadly U shaped at the base, densely and permanently hairy on the undersurface, and with three to seven bristle-tipped lobes that tend to have relatively few secondary lobes or teeth. The flowers, appearing from late April to May, are unisexual, with female flowers occurring singly or in pairs and male flowers arranged in much more conspicuous clusters of long, drooping catkins. The fruit is an acorn averaging about 1-1.5cm in length, and is covered about of its length by a scaly saucer-like cup.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
PABS
The PA Biological Survey considers southern red oak to be a species of special concern, based on the relatively few occurrences that have been confirmed and the small state range. It has a PA legal rarity status and a PABS suggested rarity status of Endangered. Fewer than fifteen populations are known from the state.
Habitat
The species grows in well-drained woods, thickets, serpentine barrens, and dry slopes.
Survey Dates
Flowers April - May; leaves distinctive
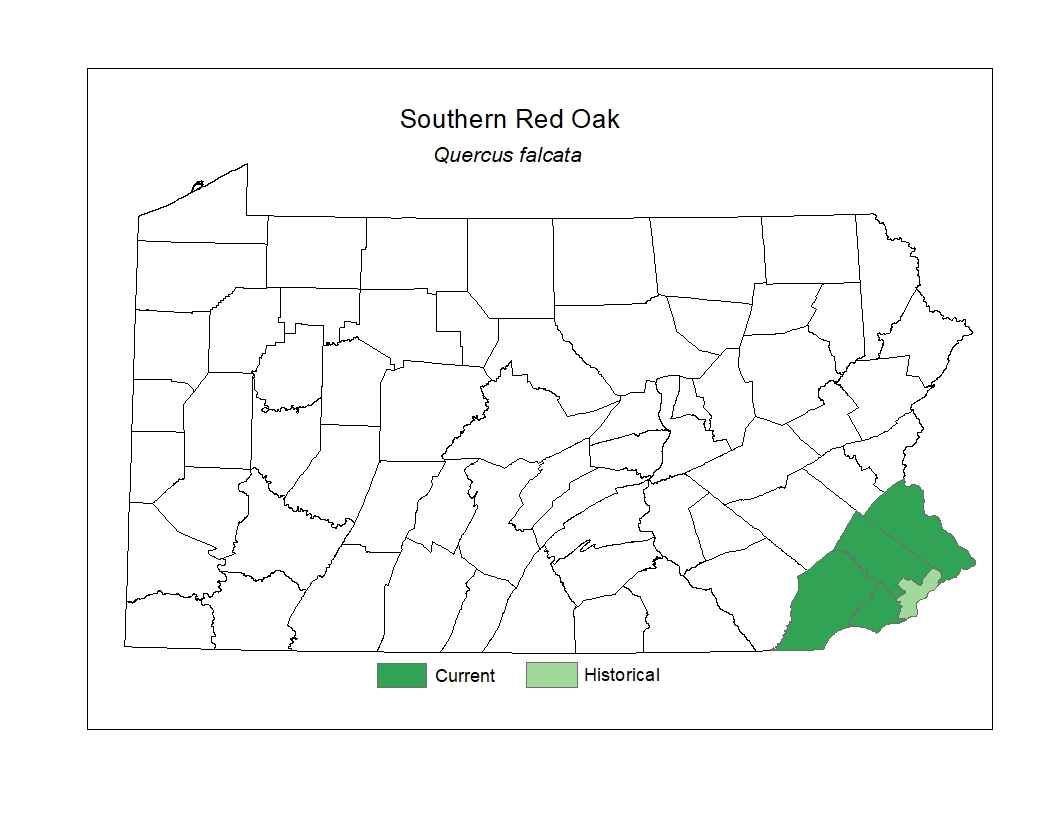
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, it represents a southerly species and has been documented historically in a few southeastern counties.
Threats
The known populations of southern red oak are threatened by habitat loss, invasive species, and in some locations, excessive browsing by deer.
Management
Establishing buffers around fragmented forested habitat and removal of invasive species will help to maintain populations.
Conservation Status Map
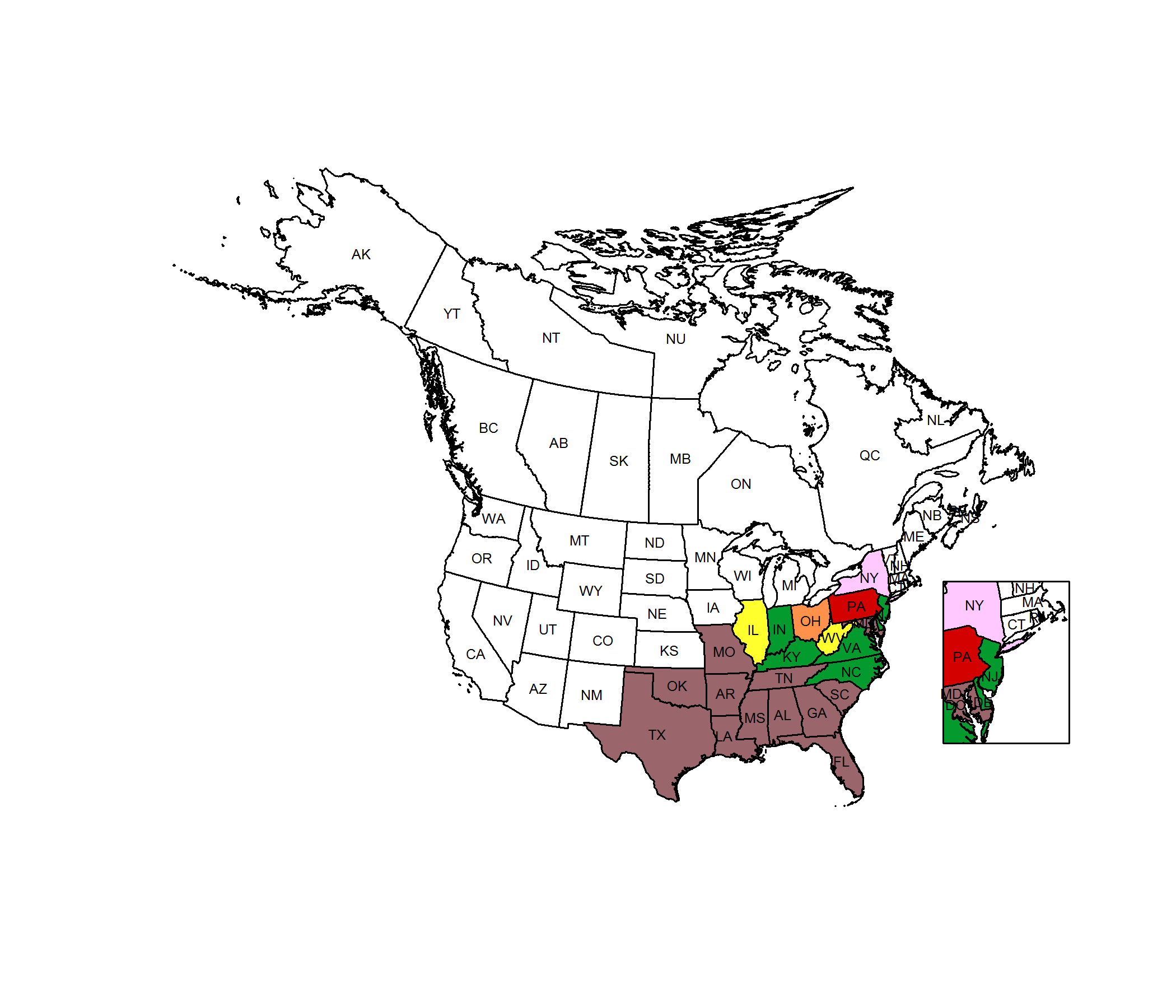
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://www.museum.state.il.us/muslink/forest/htmls/trees/Q-falcata.html
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







