 Species Factsheets
Species Factsheets
Agalinis auriculata
Eared False Foxglove
State Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
PBS Status: Pennsylvania Endangered (PE)
Federal Status:
Global Rank: G3
![]() rank interpretation
rank interpretation
State Rank: S1
Did You Know?
This species is a hemi-parasite that obtains nutrients from two species of sunflower.
Description
Eared false foxglove (Agalinis auriculata) is an herb with a simple hairy stem 30-40cm high. The purple onch flowers bloom in the upper leaf axils, forming a leafy spike. Blossoms are funnel-shaped with five lobes and four stamens. One pair of stamens is longer than the other. The fruit is a capsule about 1.3cm long. Eared false foxglove is so named because the uppermost leaves have lobes that stick out at the base, reminding botanists of earlobes.
Rank Justification
Critically imperiled in the nation or state because of extreme rarity (often 5 or fewer occurrences) or because of some factor(s) such as very steep declines making it especially vulnerable to extirpation from the state.
Habitat
This plant grows in prairies, open dry woods and fields.
Survey Dates
Flowers late August - September
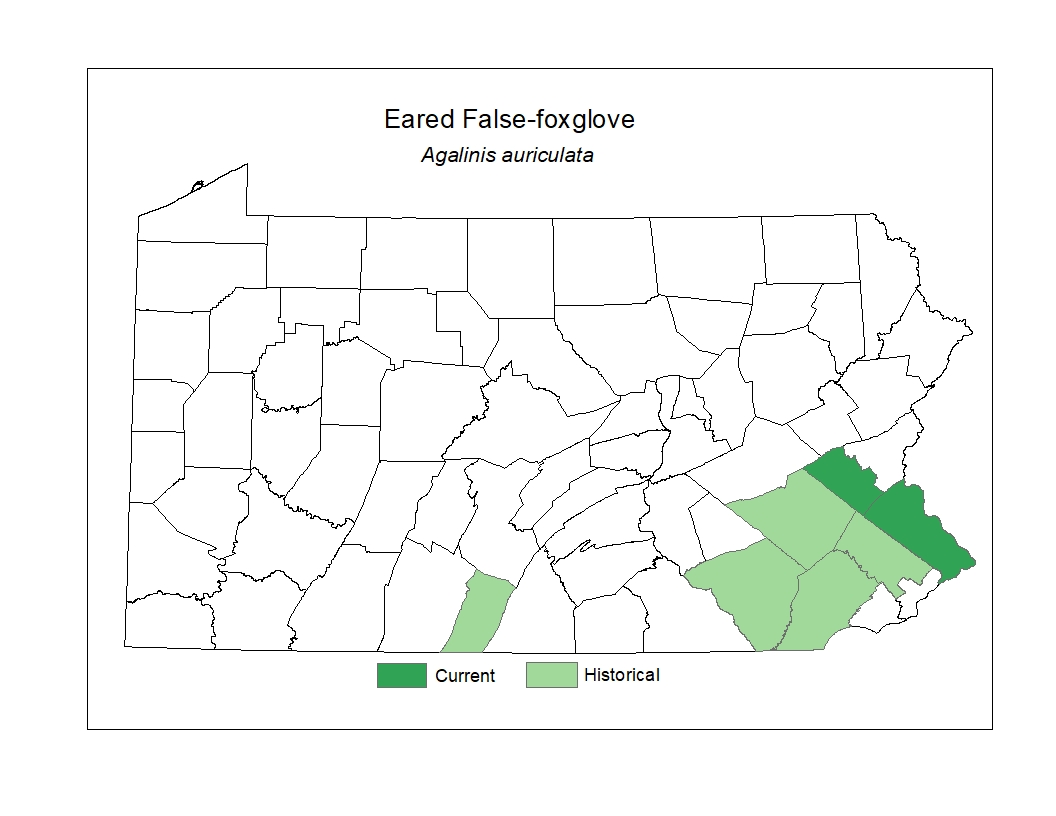
Distribution
In Pennsylvania, it is currently surviving at only two locations, on limestone gravel on the edge of an abandoned zinc mine. This species is extremely uncommon, with an historical range extending from northern New Jersey, across Pennsylvania and Ohio, to southern Minnesota, south to Virginia, Alabama, Tennessee and Missouri. A second species of Agalinis grows from Kansas south to Texas.
Threats
Habitat destruction for development is the leading cause of this species decline.
Management
Eared false foxglove is a candidate for listing under the Federal Endangered Species Act. It is one of five species in Pennsylvania to receive funding for status survey and monitoring work through a cooperative agreement with the USF&WS. A 5 year plan has been developed to search for historical populations and to protect known sites. Environmental assessments using PNDI will help to avoid impacts to any new and existing plant locations.
Conservation Status Map
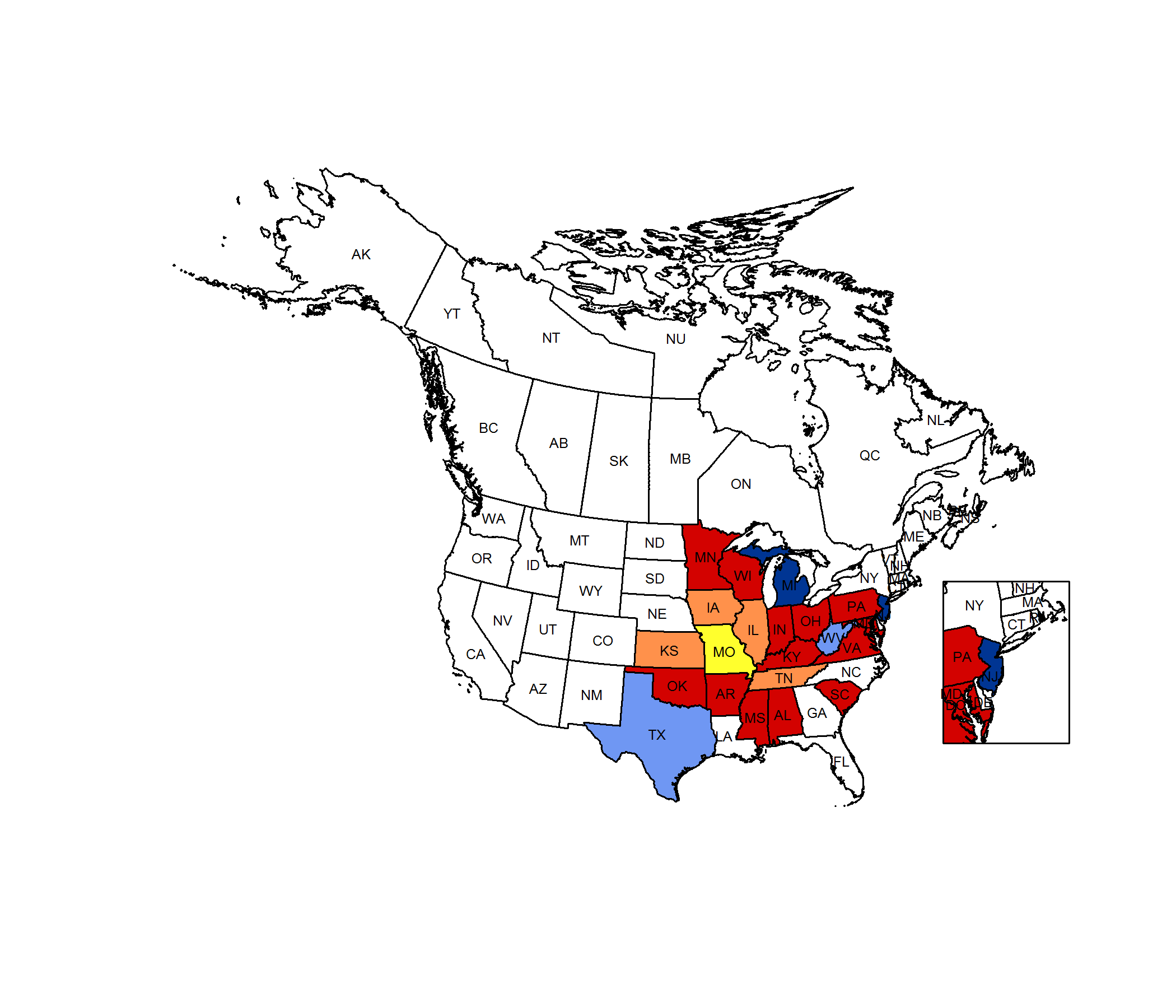
NatureServe. 2017. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available https://explorer.natureserve.org.
https://dnr2.maryland.gov/wildlife/Pages/plants_wildlife/rte/rteplantfacts.aspx?PID=Earleaf%20False%20Foxglove
- NatureServe. 2018. NatureServe Explorer: An online encyclopedia of life [web application]. Version 7.1. NatureServe, Arlington, Virginia. Available at https://www.natureserve.org/explorer
- Pennsylvania Natural Heritage Program. 2018.
- Rhoads, A.F. and W.M. Klein, Jr. 1993. The Vascular Flora of Pennsylvania. American Philosophical Society, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Rhoads, A.F. and T.A. Block.
- 2007. The Plants of Pennsylvania: An Illustrated Manual. 2nd edition. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.







